- Radiology
- Hits: 5695
Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging (D.I.T.I.) Section
A Non-invasive thermal biologic diagnostic test that assesses problems such as nerve irritation, soft tissue injuries, musculo-skeletal disorders and circulatory disorders which are often interrelated. Thermography does not show pain
because pain is a perception. It does, however show the thermal dysfunction that correlates closely with pain syndromes as well as normalization when the healing process takes place. It provides the clinician with helpful medical information in the differential diagnosis of complex pain syndromes, especially reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD).
It is based on the principle that all biologic systems emit heat energy in the form of of electromagnetic radiation, convection or conduction. It measures the body’s heat emission pattern by providing a heat map of the body that can be produced either by conduction or radiant energies reflecting cellular metabolism coming under micro euromuscular
control by pattern recognition. Thermography offers a scientific advancement for the clinician in detecting neuropathic, myofascial, circulatory, skeletal and psychogenic pain.
PRINCIPLE
At temperature above absolute zero ( -273 “C ) all bodies radiate infrared (heat) energy. Thermal energy is proportional to a molecular activity and metabolism. When focused on a sensitive detector shielded from ambient heat
by immersion in liquid nitrogen or other coolants, the electromagnetic IR ( Infrared ) signals from the body can be converted into electronic signals and processed to form a real time reproducible picture. This can be photographed
or videotaped for permanent patient record and comparative serial studies
CLINICAL BENEFITS OF THERMOGRAPHY:
- Radiculopathy
- Non-radicular muscle and fascicular disorder (muscle spasm, ligament and muscle tear or sprain, myofascial
- syndrome)
- Peripheral nerve injury
- Hyperhidrosis
- Entrapment neuropathy
- Reflex sympathetic dystrophy (Sudeck’s Atrophy)
- Inflammatory (arthritis, bursitis, rheumatism, synovitis, tendonitis)
- Post-Operative (procedural follow-up)
- Psychological (malingering, hysteria,
- migraine)
- Screening (pre-employment)






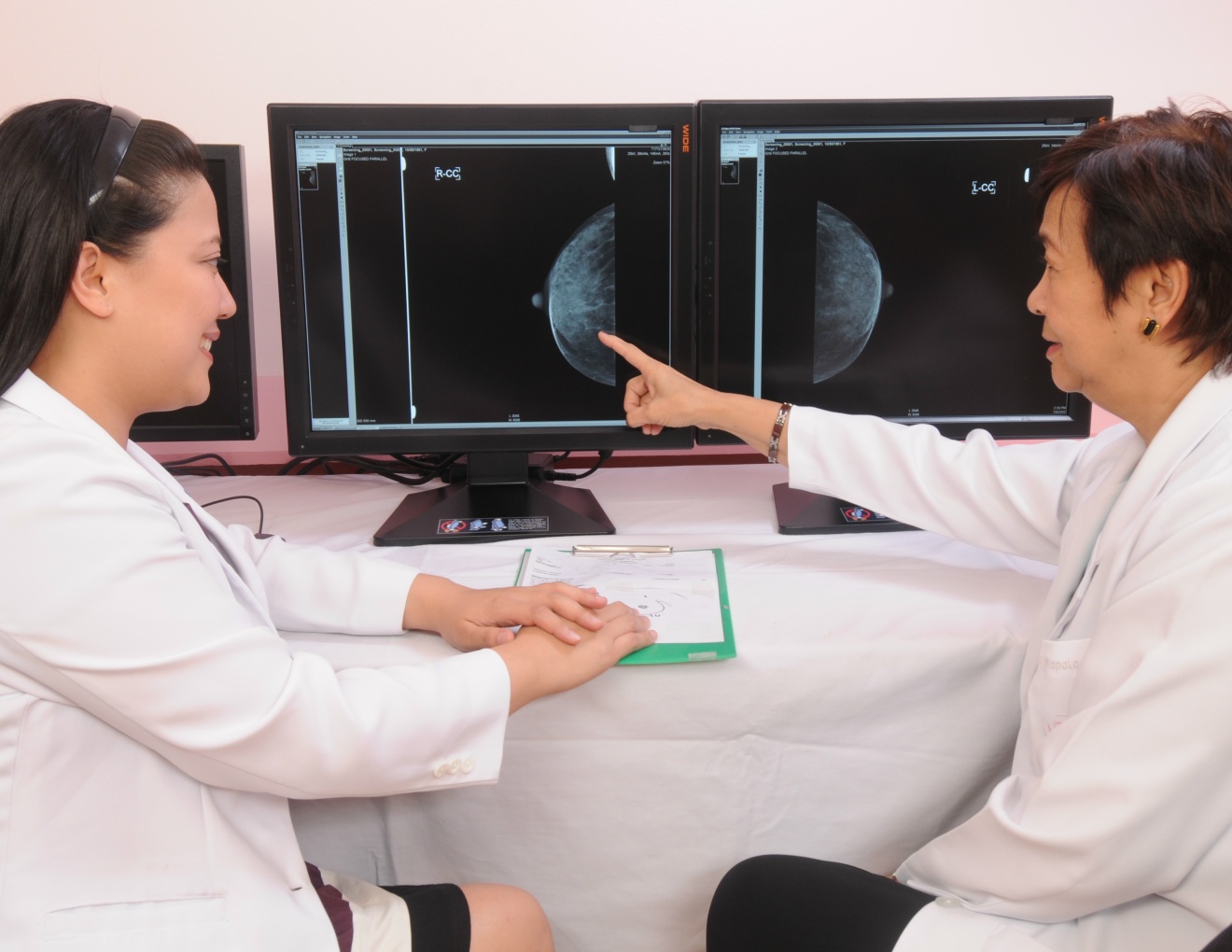




 MRI or Magnetic Resonance Imaging is the latest and most modern non-invasive state–of-the-art diagnostic modality used by physicians to obtain vital information about a patient to guide them in their treatment. MRI utilizes magnetic fields, radio waves and computers to generate multi-planar images of the body.
MRI or Magnetic Resonance Imaging is the latest and most modern non-invasive state–of-the-art diagnostic modality used by physicians to obtain vital information about a patient to guide them in their treatment. MRI utilizes magnetic fields, radio waves and computers to generate multi-planar images of the body.



.jpg)







 Laboratory.jpg)









 Section.jpg)






